MGSM MALAYSIAN GRADUATE SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT
SWOT
ANALYSIS ON MOTOROLA
PREPARED
BY:
NG KAH
SHAN (GM00734)
YANG
YUNG CHIANG (GM00747)
ZALIRA
A. RAHMAN (GM00751)
DATE:
APRIL 17, 2000
MANAGEMENT
5111
ORGANIZATION
AND BUSINESS MANAGEMENT
DR. ABU
BAKAR MOHD. YUSOF
CONTENT WORD COUNT = 3298
Table of Contents
Chapter Page
1.0 Introduction
1
2.0 SWOT
Analysis
3
2.1
Strengths
2.2
Weaknesses
2.3
Opportunities
2.4
Threats
3.0 SWOT
Matrix and Strategies Formulation 12
3.1
Strength
& Opportunities Strategies (SO)
3.2
Weaknesses & Opportunities Strategies (WO)
3.3
Strength
& Threats Strategies (ST)
3.4
Weaknesses & Threats
Strategies (WT)
4.0 Discussion 19
4.1
Most Organizations Do Not Develop Strategies for
Matched Between Opportunities and Strengths
4.2
Most Organizations Do Not Develop Strategies for
Matched Between Opportunities and Weaknesses
4.3
Most Organizations Want To Deal From Strengths
5.0 Conclusion 22
References 23
Appendix I Sig
Sigma Quality 24
Appendix II Motorola’s
Ethics 25
1.0 INTRODUCTION
The phone rings. Your pager vibrates off the bed stand. Your PowerPC boots up for the day. Your boss calls your cell phone claiming you're late. The supercomputers that operate streetlights in your community continue to keep your street safe. If not Motorola, none of these everyday occurrences would be possible. Motorola is headquartered in Schaumburg, Illinois with other operations and offices throughout US and worldwide. Motorola is well known for its innovative creation to bring quality human life. Its product range from popular cell phone, walkie-talkie, and electronics control embedded into automobile and home appliances. Motorola also well know for its quality product, it is the first cooperation obtain Six Sigma quality standard. Motorola's organization and business conduct rest on two beliefs, that guide its action worldwide -- Constant respect on individual dignity, and uncompromising integrity.
Motorola has three major
business sectors, communication Enterprise (CE), Semiconductor Product Sector
(SPS), and Integrated Electronics System Sector (IESS). CE aligns Motorola's
communication into one coordinated unit that provide integrated communication
to the world's consumer. The CE product
from cellular phone, digital video, IP telephony, telecommunication network
solution, and more. Motorola's SPS build the most seamless portfolio's embedded
core technologies in semiconductor industry. The products range from
microcontroller, digital signal processor, memories, and microprocessor. SPS is
the world No.1 producer of embedded solution.
IESS is a leading provider of electronics components and system for
customer who integrates into their own products. The customers are increasingly
relying on electronics experts to deliver more complete, feature-rich system
solution. Figure 1 shows the business
structures of Motorola.
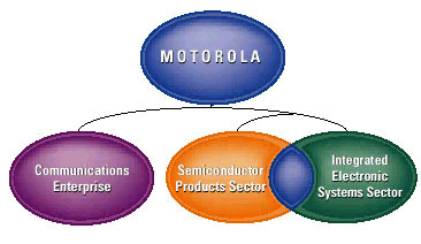
Figure 1: Motorola Business Structure
(Source: Motorola 1999 Annual Report)
2.0
SWOT ANALYSIS
2.1 STRENGHTS
2.1.1 Technology Innovative (S1)
Motorola technology is
always driven by market demand and innovation idea. It is the first company introduces two-ways radio, cellular
phone, and embedded processor in the world. Its SPS also introduced the
thinnest transistor that applied to the semiconductors. Motorola has research
laboratories all over the world working on innovative research and development
projects.
2.1.2
High Quality Product (S2)
Motorola is the first
manufacturing company to obtain Six Sigma quality standard (appendix I).
Motorola are broadening and integrating the pursuit of quality. Motorola’s ISO
9001 status has guaranteed its international quality standard.
2.1.3
Total Customer Satisfaction (S3)
"Motorola exists to
satisfy its customers".[1] It reacts positively to the
customers’ complaints to improve its competitive advantage.
2.1.4
Diversification (S4)
Motorola are producing a
wide range of products from semiconductor to wireless communications technology
products and home-automation. Examples
are cellular phone, walkie-talkie, microcontroller for microwave oven and
camera, car electronics, etc.
2.1.5
Well Developed Information System (S5)
Motorola has a state-of-the-art information system to keep tract all the information that is being used in the organization. It has central database linked to the accounting, finance, and human resource departments worldwide. The computerized manufacturing system also keeps track the product flows and history.
2.1.6 Professional Working Culture (S6)
Motorola have created a
professional working culture within the organization over the world. It treats
all the employees with respect and fairness at all times regardless their
seniority, level of management, etc. It built-up a constant respect culture
between the employees to make sure all of Motorolans are treated with dignity,
as everyone of us would treat ourselves.
Besides, all of the
Motorolans are educated with "uncompromising integrity". It is a way to enhance the
organization's achievement by maximizing the employees' performance. All of
them are being trained to stay true to what they believe. They adhere to
honesty, fairness and "doing the right thing" without compromise,
even when circumstances make it difficult. [2]
2.1.7
Globalization (S7)
Motorola is a worldwide
organization. It has been designated as the intended prime contractor for
Teledesic, which plants to offer fixed service with multimedia capabilities,
including data, video and voice, to every point on earth. Motorola have
operations and offices all over the world.
2.1.8
Highly Social Responsible and Environmental Friendly (S8)
Motorola is a responsible
citizen in all the communities where it does business. It serves society by
providing life-enhancing products and services at a fair price. Motorola
Foundation and Motorolans throughout the world provide generous financial and
voluntary support to thousands of worthwhile community growth.[3]
Motorola is an environmental
friendly manufacturing organization that complies all applicable environmental
laws in all countries which it conducts operations. It is committed to protect
the environment by minimizing the environmental impact of its operations and
foster a sustainable use of the world's natural resources. Motorola has set its
own environmental policies and program to encourage the Motorolans to notify
the management if hazardous materials come into contact with the environment or
are improperly handled or discarded.
2.1.9 Moral and business Ethic Practices (S9)
Motorola's "Code of
Business Conduct" is a guide to help all the employees to live up to the
organization's high ethical standards by highlighting them some key issues of
ethics. This code of business conduct is gone beyond the legal minimums.
The ethics practices
included in code of business conduct included management ethics, employment
ethics, business ethics, legal ethics, and community moral. (Refer to Appendix
II)
2.1.10 Famous
Brand Name (S10)
Motorola is recognized as a well-established global leader in providing high quality products in integrated communications solutions and embedded electronics solutions. These include wireless communications technology, semiconductor, and electronics system products.
2.2 WEAKNESSES
2.2.1 Inaccurate Stock Control and Product Forecast System (W1)
Motorola involved in a
diversified business environment has to look after the two main sectors in
their major organization i.e. semi-conductor and cellular telecommunication.
Their product forecast system may not be accurate as production is very much
dependent on the anticipated quantity by the customers as they are towards the
customer driven solution provider.
2.2.2 High R&D expense (W2)
Being the main player in
fast changing technology, Motorola has eventually invested US$ 3.4 Billion[4]
to enhance its capability to produce new research and development program in
year 1999.
2.2.3 Complex Decision-making Process (W3)
Being active in the global
business environment, Motorola organizational structure is much more complex
compared to other international organization. The layers of decision-making for
this organization has to go through several approval levels hence delayed
decision-making process.
What this organization has
done is to have a more functional approach in getting the decision made fast
enough to have the end product to be established. Showed in the weaknesses when Motorola missed the bus of
revolution technology in 1997.
The impact of this loss
opportunity is the market share reduction by about 29% with the newly
competitors involvement from companies such as Ericsson and Nokia in cellular
telecommunication.
2.2.4 Ineffective Project Management (W4)
Several major projects
involving large investment was unsuccessful as it was very much dependent on
other manufacturing companies which produces finished goods such as IBM and
Macintosh computers.
Failure to meet the target
of a project was shown in the recent year with crash of Iridium LLC, a
satellite telecom company backed by Motorola. This inefficiency has cost this
company approximately US$55 million and 66 satellites with minimal benefit. [5]
2.2.5 Higher Production Costs (W5)
As the market leader in the manufacturing sector, Motorola has proven to be the well-known label in the world. With the higher quality product standards Motorola has actually pay more for the cost of the products. On another hand, production cost is high because the large organization overhead and manufacturing activities in US and Europe.
2.2.6 Legacy Products (W6)
As part of the organization
culture, Motorola has practiced 'Total Customer Satisfaction’. In the fast changing technology world, this
entertained the customers’ requirement of legacy products.
2.3 OPPORTUNITIES
2.3.1 Fast Growing in Wireless Communication (O1)
The projected number of
wireless phone users worldwide by year 2002 will exceed 1 billion.[6]
Wireless communication provides a convenient solution for communication,
cheaper solution for underdeveloped area as it saves cost of cabling and pole.
The third generation of wireless communication will not only comprise of voice
transmission, but also data transmission.
2.3.2 International Growth Opportunities (O2)
The world's last and largest marketplace -- China, is opening up her market to foreigner. Under WTO agreement, China will remove the restriction on foreign investors in the area of wireless communication. Also, tariff will be reduced or remove for imported goods.
2.3.3 Lower Manufacturing Cost in Asia Pacific (O3)
The labor cost in Asia is
relatively cheaper than in US and Europe.
Taiwan, Singapore, and Malaysia can provide high technology labor force
with lower labor cost. On the other hand, the number of manufacturing
subcontractor and foundries for electronics industry is increasing in Asia
region. The foundries can take the low-end assembly process to high-end wafer
fabrication in a cost effective manner.
2.3.4 Increasing Demand on Intelligent Smart Chip (O4)
When the armed house is being broken in by thief, the security system will not only trigger the alarm, but also make phone call to owner's cellular phone and community police station. The advance electronics features require more sophisticated electronics control system. The estimated number of smart chips to be sold globally in next 5 years is 50 billion.[7]
2.3.5
New Electronics Control System Embedded with Car (O5)
The annual worldwide demand projected for automotive electronics by 2002 will be US$ 26.5 billion. The embedded electronics system includes fuel injection controller, car alarm, Global Positioning System (GPS), etc.
2.3.6
Advance TV Services and Home Networking (6)
Estimated US cable industry revenue by 2005 through deployment of digital cable, high speed internet, and telephone via broadband will be US$ 80 billion.[8]
2.4
THREATS
2.4.1 Rapid
Technology Cycle (T1)
Wireless technology change every 5 years, semiconductor technology change every month. According to Moore's law, the speed of microprocessor doubled every 18 months. The electronics industry is the rapid changing industry. If company cannot catch up with technology change, it will be left behind.
2.4.2 New
Entrants in Wireless Communication Industry (T2)
Five years ago there are only Motorola, Ericsson, and Nokia in cellular
phone market. Nowadays, Sony, Alcatel, Panasonic are entering the cellular
phone market. More and more new entrants are becoming key player in the
industry because its prospect and profit margin.
2.4.3 Competition
from Competitors (T3)
Most products can be substitute with another product with similar
functionality and features, especially general function product like cellular
phone from competitors. Competitors are moving aggressively to gain market
share, too.
2.4.4 Changing
of Customers' Needs (T4)
Demands of customers always changes due to the environment change.
Customers change their requirement because of new technology and feature-rich
products offered by other vendors.
3.0 SWOT MATRIX AND STRATEGIES FORMULATION
SWOT MATRIX is an important matching tool that
helps us to develop 4 major strategies, i.e. SO Strategies, WO Strategies,
ST Strategies, and WT Strategies for the analyzed organization. It
is a nine-cell table that shows the four keys factors (strengths, weaknesses,
opportunities, and threats) and four developed strategies. (Please refer to
Table 1: SWOT MATRIX FOR MOTOROLA)
3.1
STRENGHTS & OPPORTUNTITES STRATEGIES
(SO STRATEGIES)
These strategies are formed by using
the organization's internal strengths to take advantage of external
opportunities.
3.1.1 Empowerment in Asia Market (S1,S2,S7,S7,S8,S10,O2)
Penetrate the China market through its teamwork strategy.[9]
This organization's competency helps to create an environment of empowerment in
culture of participation. China is focused to be an open market through WTO, it
is a great opportunity for Motorola to crap a bigger market share of the
worldwide telecommunication industries.
Table 1: SWOT MATRIX FOR MOTOROLA
|
|
STRENGTHS – S
|
WEAKNESSES – W
|
OPPORTUNITIES – O
|
SO STRATEGIES
|
WO STRATEGIES
|
THREATS –T
|
ST STRATEGIES
|
WT STRATEGIES
(W5-T1/T2/T5)
|
3.1.2 Forward
Integration Within Manufacturing Sectors (S1,S2,S3,S4,S7,S10,O4,O5)
With the strongly
organization fundamentals, it could build a forward integration in the
telecommunication industries, home appliances product industries. The organization easy to foreseen the
potential development by getting closer to the ultimate customers
3.1.3 Enhance Organization’s Competitive Advantage (S3,S4,S5,S7,S9,O3)
Increasing number of
foundries in Asia enhance Motorola negotiation power to choose for a better
subcontractor with best cost-to-quality performance.
3.1.4 Build a Partnership with Supplier and Customer
(S1,S5,S10,O1,O4,O5)
To have more cooperation between the supplier and
partners is one way to stay competitive by influencing them to generate a
greater market of Motorola.
3.2
WEAKNESSES & OPPORTUNITIES STRATEGIES
(WO STRATEGIES)
This strategy focused at
improvement of internal weaknesses by taking advantage of external
opportunities of the organization.
3.2.1 Formulate
a Strong Analysis Team (W1,W4,O1,O2)
Existing stock control and product forecast system inaccurate in the
predicting the future of technology. To overcome this, formation of team of
analysts wireless communication background would help to predict better
performance.
3.2.2 Strategic
Alliance (W2,O4,O5)
With the increased in growth of telecommunication, Motorola has
invested about 10% of total sales amount on research and development, which is
essential to maintain its market share.
As Motorola generally
produces the semi-finished products such as controller, allowing more participation
and expansion of existing diversity in manufacturing. Home appliances companies
may agree to joint new ventures with Motorola and allow the growth in
technology advancement of Motorola.
With the new electronic
control-system embedded in cars has also allowed Motorola to venture into the
motoring activities and alliances with the car manufacturers. These strategies
can be met if Motorola evaluates the opportunities on strategic alliances with
other industries.
3.2.3 Formulate a Team with Expertise in Business Negotiation
(W3,O1,O2)
Realizing the global
opportunity available, Motorola has ventured into fast growing and
international business especially in the Asia Pacific region. This will allow
expansion in the market of semiconductors in the developing countries. With Motorola involvement and plant set-up
in Malaysia and China, Motorola has the capability to produce and manufacture
products to meet the regional customer demand.
With the fast product cycle Motorola can address its weaknesses with
formation of decision analysis team consist of regional experts.
3.2.4 Business Expansion to Growing Region (Asia Pacific) (W5,W6,O3)
With the existence of the
number of sub-contractors or foundries in Asia Pacific region, Motorola could
address its production costs to lower rates, which could provide the optimal
return for the company. This can be
accomplished with the new-plant setups in developing regions that allow the
sub-contractors to manufacture parts such as multi-controller carrying Motorola
trademark. Hence, with the company establishment in the sector, will
essentially create customer support and awareness for Motorola. Since it has
established operations worldwide, it is much more feasible to have several raw
materials shipped from other regions. For example, setting up of the business
in Malaysia is much cheaper compared to the total cost for raw materials
generated in other regions.
3.3 STRENGHTS
& THREATS STRATEGIES (ST STRATEGIES)
3.3.1 Build a Horizontal Integration (S1,S2,S4,S10,T3)
In view of the
organization's innovative competitive advantage and the aggressive strategies
from the existing competitors. Motorola should enter into new and innovative
partnerships and aligning with best-of -breed providers in multiple industries,
often with the best competitors.
3.3.2 Shorten the Rate of New
Product Formation (S1,S2,S5,S6,S7,S8,S10,T2,T3)
In order to stay
competitive, the organization needs to react fast to stop the new entrants and
the threats from the existing competitors. One the strategies is to shortened
the cycle time of creating new products in order to bring them to market
3.3.3 Develop Renewal Program to Extend Product’s Life
(S1,S4,S8,S9,S10,T1)
Develop renewal program to
overcome the rapid technology cycle. Example, develop new model of cellular
phone with more features and advance technologies to extend its useful time.
3.3.4 File Appropriate Pattern (S1,S3,T2,T3,T3)
File appropriate pattern to
protect the organization’s innovation and creation. Motorola holds 21,807
patterns in year 1999.[10]
3.3.5 Shift Toward Market Driven Strategy (S1,S2,S3,S8,S9,S10,T4)
Form-up a strong market
survey team to conduct several analyses on the customer needs. Built a good
relationship with supplier and customers to have more understanding on the customers
needs.
3.4
WEAKNESSES & TREATES STRATEGIES
(WO STRATEGIES)
These strategies are mainly
defensive strategy with the target to reduce internal weaknesses and the
external forces such as environmental threats.
3.4.1 Joint Venture and Strategic Alliance (W5,T1,T2,T5)
New entrants in wireless
telecommunication have also result in threats for Motorola with fear in losing
its market share worldwide. With economies of scale factor, Motorola can ensure
competitiveness with formation of alliances/agreement with their competitors.
With the fast changing
customers’ requirement for electronic products, Motorola need to maintain its
pace in the changing technology and lifestyle. The defensive strategy is to
have a customer’s services center to cater for customer needs.
3.4.2 Concentrate Effort in Marketing Strategy (W5,T3,T3)
With more players in the
same industry such as Phillips, Siemen has imposed another threat for Motorola
to be competitive. This led to more aggressive strategies from competitors and
more attractive substitute goods available in the market.
3.4.3
Eliminate Legacy Product Production (W6,T1,T2)
Motorola has the option to
stop manufacturing legacy product in view of rapid changing technology and
aggressive new entrants. This strategy eliminates the unprofitable production
and concentrate production in its competitive product line. However, in order
to satisfy some customers’ need, Motorola can transfer those production lines
to foundries or subcontractors.
4.0 DISCUSSION
4.1 MOST ORGANIZATION DO NOT DEVELOP
STRATEGIES FOR MATCHES BETWEEN OPPORTUNITIES AND STRENGTHS
When too many weaknesses are realized, the company tends
to overcome all the weaknesses in order to make them strengths. When the
organization faces major threats, they will seek to avoid them in order to
concentrate on opportunities.
Strength and opportunities
strategies are improvement issues while threats and weaknesses strategies are
survival issues. Usually company will focus the survival issue to overcome its
weaknesses and make them to be strengths. Also, it will apply strategy to
reduce threats from environment. Only after all these, the company can utilize
its strengths in a world with fewer threats.
For example, Motorola matched its strength in analog
communication technology with cellular phone market opportunity. However, this
strategy failed because it foregoes its weaknesses and threats in digital
communication technology. This resulted in the reduction of Motorola's market
share from 46% to 29%. Motorola completely missed the digital revolution in
cellular phones in 1997.
Following this experience, Motorola has advanced their
involvement in digital communication technology to be more competitive.
4.2 MOST ORGANIZATION DO NOT DEVELOP
STRATEGIES FOR MATCHES BETWEEN OPPORTUNITIES AND WEAKNESSES
Every
opportunity comes together with threat, an organization need to overcome the
threat before it can utilize the opportunity. WO strategies aim at improving
internal weaknesses by taking advantage of external opportunities. An
organization has to develop intensive programs to overcome its weaknesses. It
is kind of risky and costly because the opportunity is not secured after the
weaknesses are overcome. Therefore, most organizations will not develop such
strategies.
In
term of time factors and efforts, strategies that require vast change in
cooperate culture may not be favorable. This is mainly due to extensive
duration required to complete such task, and more efforts and longer man-hours
needed for the change to take place.
4.3 MOST
ORGANIZATION WANT TO DEAL FROM STRENGTHS
Company that focused
its strategy on strength mainly because it is proven to be the fastest solution
available. Furthermore, the implementation of strengths has already existed in
the organization, and it does not require any investment to be carried out.
Motorola has also become the established leader in the industry and be the market leader. Strength has become a reputable source available. Another reason why strength is more favorable among the companies is because this helps to build the confidence in pursuing their goals. Typically companies realized their internal power and strengths and with this strong background, they are more likely to success. Also, the capability and creditability of their strength need not be questioned as they are proven one.
5.0 CONCLUSION
As an established multinational COMPANY, Motorola does certainly have more strengths than weaknesses. However, to become even more competitive and keep stay in the marketplace, it need to overcomes its organization’s weaknesses and environment threats, especially it is operating in the most competitive industry. Eventually the WT strategies will transform to SO strategies as the organization and environment are improved. The SO strategies can only be utilized after the weaknesses and threats have been reduced.
References
- David, Fred (1997), Concepts of Strategic Management 6th
Edition, Prentice Hall
- Hellriegel, Don (1998), Management 8th Edition,
South-Western Pub
- Kreitner, Robert (1997), Management 7th Edition,
Houghton Mifflin College
- Miller, Alex (1998), Strategic Management 3rd Edition,
McGraw-Hill
- Motorola Homepage (2000), Motorola Inc., Available at: http://www.motorola.com
- Roth, Daniel (1998), Burying Motorola, Fortune Magazine July 6,
1998, Available at http://www.fortune.com/
- Roth, Daniel (1999), Motorola Lives!, Fortune Magazine September
27, 1999, Available at http://www.fortune.com/
- Tetzeli, Rick (1997), And Now for Motorola’s Next Trick, Fortune
Magazine April 28, 1997, Available at http://www.fortune.com/
- Schonfeld, Erick (1998), Hold the Phone: Motorola is Going Nowhere
Fast, Fortune Magazine March 30, 1998, Available at http://www.fortune.com/
- Schonfeld, Erick (1998), Hold the Phone: Motorola is Going Nowhere
Fast, Fortune Magazine March 30, 1998, Available at http://www.fortune.com/
Appendix I: Six Sigma Quality
Six Sigma is a set of quality measurement scale
(ranging from 2 to 6), describes defects in parts per million. It's eliminating
defects to the level of 1 per 3.4 million opportunities, or a process that is
99.99966% defect free. A key theme in Six Sigma programs is the reduction of
waste.
Appendix II: Motorola’s Ethics
Management Ethics
The managers in Motorola are expected to lead
according to its standards of ethical conduct, in both words and actions. They
are responsible for promoting open and honest two-ways communications, and must
be positive activists and role models who show respect and consideration for
each of the organization's associates. Managers are also ordered to be diligent
in looking for indications that unethical or illegal conduct has occurred in
the organization.
Employment Ethics
The organization is responsible to provide and
maintain a safe and healthy workplace to the employees. Motorola is committed
to keep its workplaces free from hazards.
Business Ethics
Motorola will only obtain business legally and
ethically. Bribes or kickbacks are strongly prohibited in Motorola. Motorolans
around the world are required to comply with all applicable laws and
regulations wherever they do business. All the Motorola's products are markets
at high quality standards with fair prices. In order to build a long-term
relationship with customers, Motorola always practices honesty and integrity to
the business partners by providing accurate and truthful marketing and
advertising information. They make sure all the customers’ information are
highly private and confidential to the public. The organization has set up a
law department and EthicsLine to guide the Motorolans to act ethically in the
business world.
Legal Ethics
Motorolans are expected to cooperate with reasonable requests for information from government agencies and regulators, and to consult with the organization's law department before responding to any non-routine requests. All information by the organization are accurate and truthful. The organization keep all the documents and records including those information which might response to the legal investigation or other lawful request.
Community Moral
All individual are free to carry out their orders
according to their own moral and religious beliefs. None of the Motorolans can
pressure another employee to express a view that is contrary to a personal
belief, or to contribute to or support political, religious or charitable
causes.